Investing in a company’s stock is done in order to gain from price growth, dividends, or both. To trade stocks, one must do more than merely stroll up to an exchange and purchase shares. Only authorized individuals known as brokers are allowed to trade on the stock exchange, and all transactions must go via them. Before you can start trading, you must first register with a broker. The most popular way to do this is online. This course gives you the information you need to start trading and investing on the stock market.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Stock Market
- Fundamentals of Stock Market Trading
- Understanding Stock Prices
- Factors Influencing Supply and Demand
- Essential Stock Trading Techniques
- Stock Dividends Explained
- Stock Market Indexes
- Major Global Stock Markets
- Starting to Invest with Limited Funds
- Lastly
Introduction to the Stock Market
A stock exchange acts as a central location for the daily buying, selling, and issuance of shares of publicly traded businesses. The stock market is made up of all the stock exchanges inside a country. By connecting buyers and sellers to expedite transactions, these exchanges offer a trading platform where anybody can buy or sell shares of a certain firm. For instance, if you tell your broker to find a seller of 200 Apple shares at the price you specify, the broker will forward your order to the stock market, which will connect you with the seller. The transaction will then be finished, and the broker will receive payment for their assistance.

Introduction to the Stock Market
Fundamentals of Stock Market Trading
A kind of ownership in a business is a share. You acquire a little stake in the company when you purchase a share. If a corporation has 1000 shares, for instance, and you hold 150 of them, you own 15% of the business. The fact that many companies have hundreds of thousands of shares means that your ownership may not be substantial.
Markets can be divided into two categories: primary and secondary. A firm goes public through a procedure known as an initial public offering (IPO), typically by offering shares to the general public who can then apply for them. After allocating these shares to applicants, the business normally keeps some shares for ownership purposes.
In the secondary market, where the company is not involved in the transactions, investors and traders can buy and sell the shares that the company has issued in the primary market. These take place in the marketplace face-to-face between buyers and vendors.
Understanding Stock Prices
Similar to the price of any other item, the price of a stock is established by the market’s intersection of its supply and demand. A stock’s price will drop if there is an excess supply, which occurs when more people desire to sell the stock than acquire it. This will cause sellers to reduce their asking price, which will drive down the price until supply and demand are in balance.
The price of a stock will rise because more individuals are ready to pay more for it if, on the other hand, there is a greater demand for it than there are sellers. The share price will rise as a result until supply and demand balance each other out.

Understanding Stock Prices
Factors Affecting Supply and Demand
Numerous factors that each have the capacity to boost or reduce the stock price can affect it. Some of these elements and how they affect stock prices are as follows:
- Macroeconomic factors: The state of the general economy has an impact on the stock market. Companies may struggle with greater costs and lower demand during a recession, which will drop their stock price. On the other side, a strong economy can raise stock values because of the optimistic outlook for businesses.
- Profits reports: The days before and after a firm announces its earnings are typically active times for its stock price. Investors may purchase firm shares if they anticipate strong performance, whereas shares may be sold if the company performs poorly. Additionally, dividends contribute to this process.
- Events in the industry: Significant occurrences that have an impact on the entire sector can also alter the supply and demand for a specific stock. For instance, given oil is a significant expense for airlines, a rise in oil prices may result in a decline in airline stocks.
- Technical patterns: Based on patterns and trends in historical prices, many traders use technical analysis to forecast future stock prices. This strategy may have an impact on the supply and demand of stocks on a particular day.
- Exchange rates and interest rates may also have an effect on market-wide stock prices. For instance, if a government boosts interest rates, consumers might decide to put their money in a bank instead of equities, which would cause stock values to fall. increased exchange
Essential Stock Trading Techniques
Understanding the two basic trading tactics, technical analysis and fundamental analysis, is crucial for effective stock trading. You can choose the best stocks to invest in or trade using these methods.
It’s important to distinguish between trading and investing. The objective of investing in a company is to make money over the long term through dividends and an increase in the stock price, which is frequently attained through the firm’s constant profitability, market expansion, and effective operations.
The goal of trading, on the other hand, is to make money from short-term price changes in equities during a time frame of a week, a day, or even just a few seconds.
Selecting the approach that works best for you is essential whether you want to trade or invest in the stock market.
Technical Analysis in Stock Market Trading
Understanding the two basic trading tactics, technical analysis and fundamental analysis, is crucial for effective stock trading. You can choose the best stocks to invest in or trade using these methods.
It’s important to distinguish between trading and investing. The objective of investing in a company is to make money over the long term through dividends and an increase in the stock price, which is frequently attained through the firm’s constant profitability, market expansion, and effective operations.
The goal of trading, on the other hand, is to make money from short-term price changes in equities during a time frame of a week, a day, or even just a few seconds.
Selecting the approach that works best for you is essential whether you want to trade or invest in the stock market.
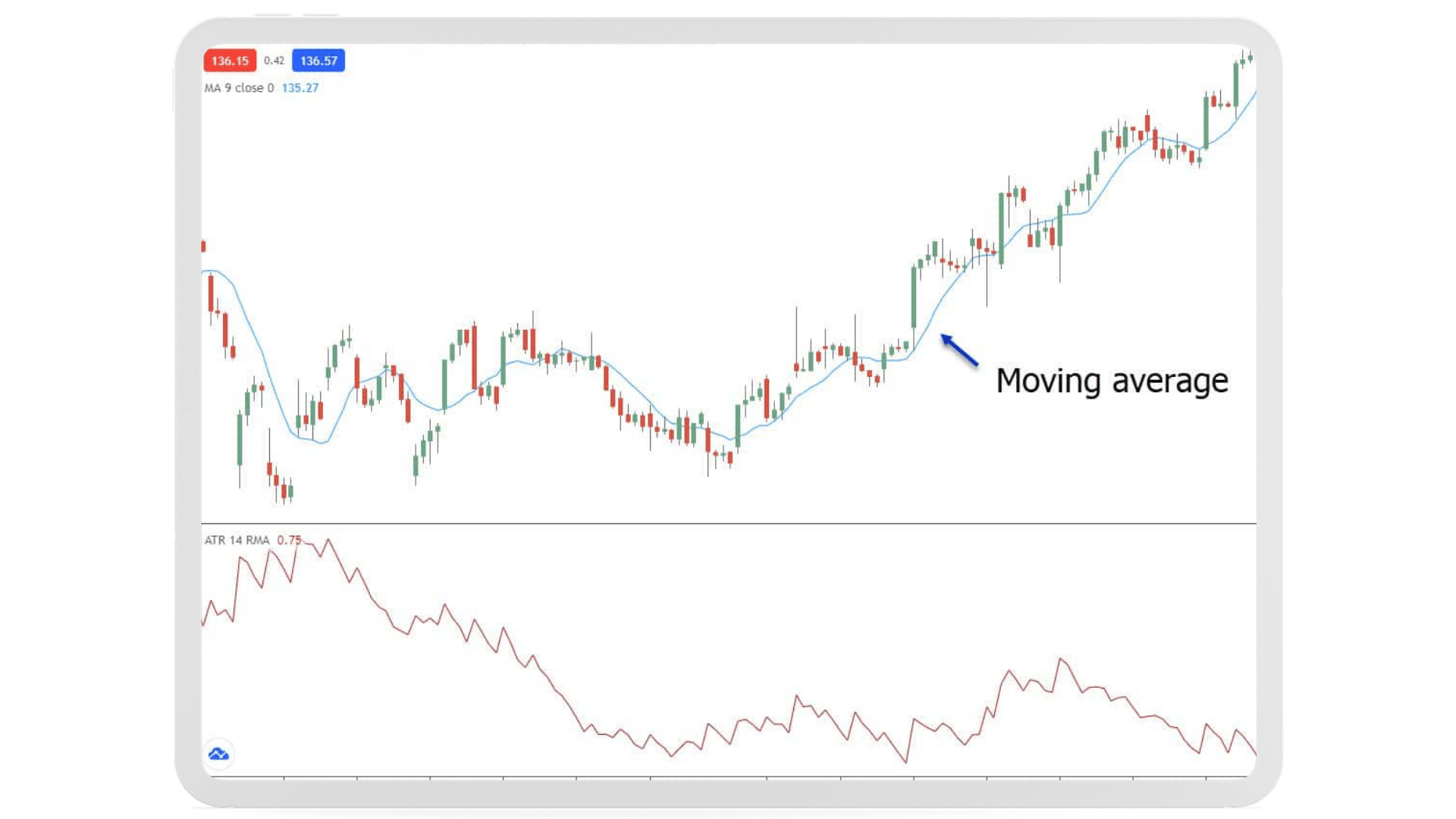

Technical Analysis in Stock Market Trading
Fundamentals-Based Stock Market Trading
Investors use fundamental analysis as a tool to assess a company’s financial standing and predict its future growth. Legendary investor Warren Buffet made this kind of analysis popular because he thought it was the secret to continually making money in the stock market over the long haul. Gaining a deep knowledge of the underlying business model that a company employs is the aim of fundamental analysis.
Investors initially examine the company’s financial accounts in order to conduct a fundamental study. This entails calculating different financial statistics to ascertain the profitability and efficiency of the business. For instance, depending on a company’s present stock price and earnings, the price-to-earnings ratio (P/E ratio) can be used to determine whether it is cheap or overvalued.
Investors examine the company’s management team in addition to its financial results. This entails looking at the organization’s structure and leadership style, as well as any claims of bribery or corruption against senior management. A sound business can be identified by a strong and moral leadership team.
Comparing the target company to its rivals is a key component of fundamental analysis. In order to determine how the target firm is functioning in comparison to its rivals, it is necessary to analyze their financial accounts. Investors could, for instance, assess whether the target company’s P/E ratio is undervalued or overvalued in comparison to its rivals.
In order to find any inefficiencies, fundamental analysis also looks at the company’s supply chain. Analyzing suppliers, service providers, and components with unusually fluctuating costs is part of this process. Investors can then determine whether the company has a sustainable business strategy and how it intends to overcome these inefficiencies.
Investors can buy shares of these companies and hold them for the long term when the fundamental analysis is finished and viable companies have been found. When the business succeeds, the share price will probably rise, giving the investor the chance to gain from owning a piece of a flourishing business.
Stock Dividends Explained
A distribution of a company’s profits to its shareholders is known as a stock dividend. Owning stock in a firm entitles you to a portion of its ownership as well as a cut of its earnings. When a publicly traded firm makes a profit, it keeps some of it for upcoming operations and distributes the rest as dividends to shareholders. Some businesses pay bigger dividends, increasing the value of their stock because both a payout and a share price gain are possible. A approach to get passive income is to invest in firms that pay out high dividends.
Stock Market Indexes
A wide range of stocks are available to trade and invest in on stock exchanges, and they can be arranged according to their sector, place of origin, and stock valuation. It’s not possible to look at every company in order to gauge how a sector as a whole is doing. Stock market indices play a role in this. An index is a collection of equities that share a characteristic, such as the S&P 500, which represents the 500 largest US corporations and provides a snapshot of the US economy. Another illustration is the US Tech 100 index, which represents the performance of the tech industry as a whole and consists of 100 of the top US technology stocks. Indexes provide a useful way to monitor entire sectors or economies and can also be used for diversification through index funds, which allow investing in the entire index in a predetermined ratio.
Major Global Stock Markets

Stock Market Indexes
There are stock exchanges in every nation where shares are issued and traded. The number of shares a firm owns is multiplied by the share price to get its market capitalisation. The total market value of all the companies whose shares are traded on a stock exchange is the market capitalization of that exchange. The following list of the top 10 largest stock exchanges worldwide, ordered by market capitalisation, is:
- ($25.6 trillion) New York Stock Exchange
- NASDAQ Stock Market (19.51 trillion dollars)
- ($6.76 trillion) Hong Kong Stock Exchange
- ($6.56 trillion) Shanghai Stock Exchange
- ($6.54 trillion) Japan Stock Exchange
- NASDAQ Euronext (5.08 trillion dollars)
- NASDAQ Shenzhen ($4.83 trillion)
- ($3.83 trillion) London Stock Exchange
- The 3.16 trillion dollar Bombay Stock Exchange
- (3 trillion) National Stock Exchange
Additionally, each exchange has its own index that comprises the biggest companies traded there. Many online brokers provide trading on numerous exchanges, allowing users to simultaneously trade on different markets.
Starting to Invest with Limited Funds
Finding an online broker and opening an account are the initial steps in starting to trade or invest in the stock market. This necessitates the submission of private data such verification of identity and address. Once your account has been set up, you can deposit money and begin buying and selling shares. There are two primary ways to do this: either by purchasing shares in person or by trading Contracts for Difference (CFDs).
Stock Ownership
Finding an online broker and opening an account are the initial steps in starting to trade or invest in the stock market. This necessitates the submission of private data such verification of identity and address. Once your account has been set up, you can deposit money and begin buying and selling shares. There are two primary ways to do this: either by purchasing shares in person or by trading Contracts for Difference (CFDs).
Trading Contracts for Difference (CFD’s)
Contracts for Difference are another choice for trading stocks (CFDs). These are derivatives, and the stock of a firm serves as the underlying asset from which their value is derived.
When you trade CFDs, you don’t actually purchase any shares; instead, you make a prediction about the direction of the company’s price movement. You could profit from buying or selling the instrument if your prediction proves to be accurate.
The majority of brokerages give you the option to trade CFDs using leverage, which allows you to use more money than you actually have. You can trade CFDs for $100 with just a $10 investment if your leverage is 10:1. Many traders are drawn to this high-risk, high-reward scenario because it doesn’t call for a significant investment.
Lastly
Think about the investment plan you want to use with your account when choosing a broker. Both share ownership and CFD trading have a variety of alternatives. It’s critical to remember that investing entails some risk, and traders should use caution when entering trades, especially when utilizing leverage. Make sure you are aware of the risk-reward ratio and the possible results of each trade, and trade sensibly.

